The terms communism, capitalism and socialism are ideologies distinct from one another.
Although capitalism is clear-cut from the rest, the same cannot be said about communism and socialism. There is a huge difference between socialism and communism too which we will make clear in this article.
Socialism and communism are often used in place of each other despite being fundamentally different from each other. The factors they share are as follows:
- Communism and socialism arose as a form of protest against the exploitation of the working class during the age of the Industrial Revolution (1760 -1840).
- The other is that they are both an alternative to capitalism.
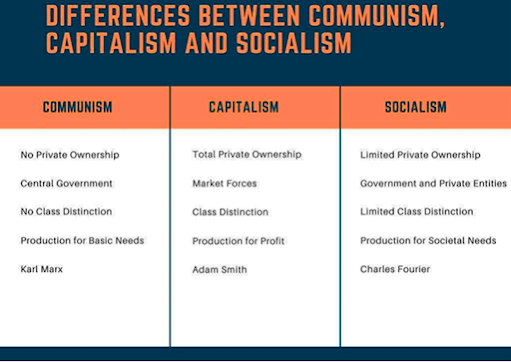
To know more about communism vs socialism, and capitalism, check the table below:
The difference between communism, capitalism and socialism is given below: Differences between Capitalism, Socialism and Communism
|
Differentiating Factors |
Capitalism |
Communism |
Socialism |
|
Ideology |
Maximisation of profit by any means necessary. It also believes in Laissez-Faire, a philosophy that emphasises leaving circumstances to run their natural course without any external intervention. |
From each according to his ability, to each according to his needs. |
From each according to his ability, to each according to his contribution. |
|
Economy Planning |
In capitalist societies, the economy is planned as per the functioning of the free markets. |
The economy is planned by the Central Government. |
The economy is planned by the central government. |
|
Ownership of Economic Resources |
Private ownership of economic resources and property is actively encouraged with little to no government intervention. |
All economic resources are publicly owned and controlled by the government. Individuals hold no personal property or assets. |
Individuals can own personal property but all industrial and production capacity is communally owned and managed by a democratically elected government. |
|
Class Distinction |
There exists a distinct class whose standing in society is measured by the material wealth in their possession. |
Class is abolished. The chances of one worker earning more than the other are nonexistent. |
Classes exist but the differences between them are greatly reduced. It is possible for some people to earn more than others. |
|
Religion |
As per the ideology, it is indifferent towards religion, but bias thus exists towards religious groups who are well-off or as rich as another religious group. |
Religion is effectively abolished. |
Freedom of religion is allowed. |
|
Welfare |
The welfare system is available only to those who have the wealth to pay for their services. |
Supports widespread universal social welfare with an emphasis on public health and education. |
The state will be for the welfare of everyone in the society without any discrimination. |
|
Origins |
The modern form of capitalism can be traced to the early Renaissance period in the 15th -16th Centuries. The wealthy merchants of Italian city-states engaged in small industry and wage-labour practices at the time. |
Although the concept of egalitarian societies existed since the time of Ancient Greece, the foundations of modern-day communism were established in 1848 by the German Philosopher Karl Marx (May 5th, 1818 – March 14th, 1883). |
The economy of the 3rd century BC Mauryan Empire was described by economists as “a socialised monarchy” and “a sort of state socialism”. It became more prominent towards the end of the 18th century and after 1848. |